* Interaction behavior plugin for child views of {@link CoordinatorLayout}.
*
* <p>A Behavior implements one or more interactions that a user can take on a child view.
* These interactions may include drags, swipes, flings, or any other gestures.</p>
*
* @param <V> The View type that this Behavior operates on
*/
public static abstract class Behavior<V extends View> {
* Called when the Behavior has been attached to a LayoutParams instance.
*
* <p>This will be called after the LayoutParams has been instantiated and can be
* modified.</p>
*
* @param params the LayoutParams instance that this Behavior has been attached to
*/
public void onAttachedToLayoutParams(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams params) {
}
* Called when the Behavior has been detached from its holding LayoutParams instance.
*
* <p>This will only be called if the Behavior has been explicitly removed from the
* LayoutParams instance via {@link LayoutParams#setBehavior(Behavior)}. It will not be
* called if the associated view is removed from the CoordinatorLayout or similar.</p>
*/
public void onDetachedFromLayoutParams() {
}
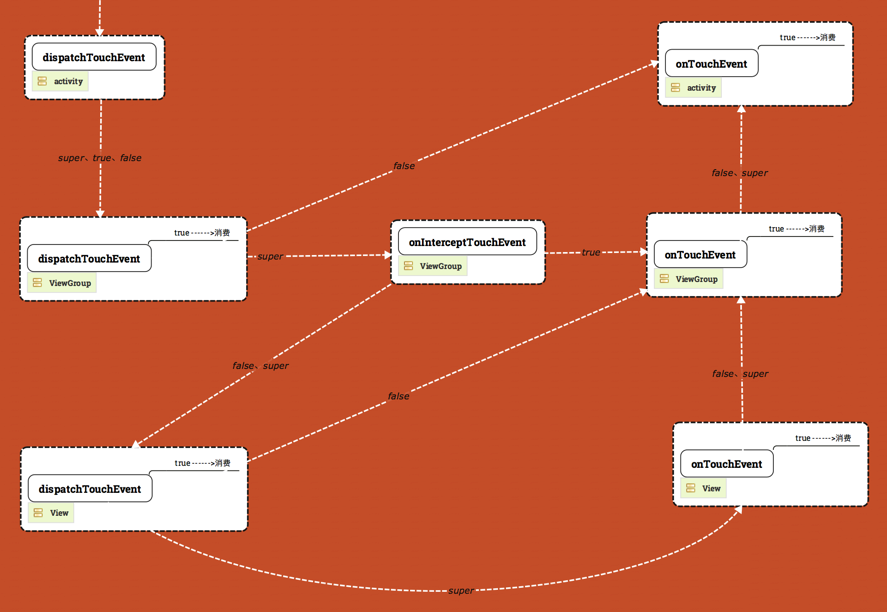
* Respond to CoordinatorLayout touch events before they are dispatched to child views.
*
* <p>Behaviors can use this to monitor inbound touch events until one decides to
* intercept the rest of the event stream to take an action on its associated child view.
* This method will return false until it detects the proper intercept conditions, then
* return true once those conditions have occurred.</p>
*
* <p>Once a Behavior intercepts touch events, the rest of the event stream will
* be sent to the {@link #onTouchEvent} method.</p>
*
* <p>The default implementation of this method always returns false.</p>
*
* @param parent the parent view currently receiving this touch event
* @param child the child view associated with this Behavior
* @param ev the MotionEvent describing the touch event being processed
* @return true if this Behavior would like to intercept and take over the event stream.
* The default always returns false.
*/
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, MotionEvent ev) {
return false;
}
* Respond to CoordinatorLayout touch events after this Behavior has started
* {@link #onInterceptTouchEvent intercepting} them.
*
* <p>Behaviors may intercept touch events in order to help the CoordinatorLayout
* manipulate its child views. For example, a Behavior may allow a user to drag a
* UI pane open or closed. This method should perform actual mutations of view
* layout state.</p>
*
* @param parent the parent view currently receiving this touch event
* @param child the child view associated with this Behavior
* @param ev the MotionEvent describing the touch event being processed
* @return true if this Behavior handled this touch event and would like to continue
* receiving events in this stream. The default always returns false.
*/
public boolean onTouchEvent(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, MotionEvent ev) {
return false;
}
* Supply a scrim color that will be painted behind the associated child view.
*
* <p>A scrim may be used to indicate that the other elements beneath it are not currently
* interactive or actionable, drawing user focus and attention to the views above the scrim.
* </p>
*
* <p>The default implementation returns {@link Color#BLACK}.</p>
*
* @param parent the parent view of the given child
* @param child the child view above the scrim
* @return the desired scrim color in 0xAARRGGBB format. The default return value is
* {@link Color#BLACK}.
* @see #getScrimOpacity(CoordinatorLayout, android.view.View)
*/
@ColorInt
public int getScrimColor(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child) {
return Color.BLACK;
}
* Determine the current opacity of the scrim behind a given child view
*
* <p>A scrim may be used to indicate that the other elements beneath it are not currently
* interactive or actionable, drawing user focus and attention to the views above the scrim.
* </p>
*
* <p>The default implementation returns 0.0f.</p>
*
* @param parent the parent view of the given child
* @param child the child view above the scrim
* @return the desired scrim opacity from 0.0f to 1.0f. The default return value is 0.0f.
*/
@FloatRange(from = 0, to = 1)
public float getScrimOpacity(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child) {
return 0.f;
}
public boolean blocksInteractionBelow(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child) {
return getScrimOpacity(parent, child) > 0.f;
}
* 一定条件下返回true即可确立依赖关系。子类重写该方法,并实现自己依赖逻辑。
* 该方法会被Behavior的LayoutParamas的dependsOn方法调用
*/
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, View dependency) {
return false;
}
*当我们的dependency发生改变的时候,这个方法会调用,而我们在onDependentViewChanged方法里做出相应的改变,就能做出我们想要的交互效果了
*当我们改变了child的size或者position的时候我们需要返回true,差不多可以理解为 当我们的dependency发生了改变,同样的,child也需要发生改变,这个时候我们需要返回true。
* 它会被dispatchOnDependentViewChanged方法调用
*/
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, View dependency) {
return false;
}
*/
public void onDependentViewRemoved(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, View dependency) {
}
* Called when the parent CoordinatorLayout is about to measure the given child view.
*
* <p>This method can be used to perform custom or modified measurement of a child view
* in place of the default child measurement behavior. The Behavior's implementation
* can delegate to the standard CoordinatorLayout measurement behavior by calling
* {@link CoordinatorLayout#onMeasureChild(android.view.View, int, int, int, int)
* parent.onMeasureChild}.</p>
*
* @param parent the parent CoordinatorLayout
* @param child the child to measure
* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec the width requirements for this view
* @param widthUsed extra space that has been used up by the parent
* horizontally (possibly by other children of the parent)
* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec the height requirements for this view
* @param heightUsed extra space that has been used up by the parent
* vertically (possibly by other children of the parent)
* @return true if the Behavior measured the child view, false if the CoordinatorLayout
* should perform its default measurement
*/
public boolean onMeasureChild(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
return false;
}
* Called when the parent CoordinatorLayout is about the lay out the given child view.
*
* <p>This method can be used to perform custom or modified layout of a child view
* in place of the default child layout behavior. The Behavior's implementation can
* delegate to the standard CoordinatorLayout measurement behavior by calling
* {@link CoordinatorLayout#onLayoutChild(android.view.View, int)
* parent.onLayoutChild}.</p>
*
* <p>If a Behavior implements
* {@link #onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout, android.view.View, android.view.View)}
* to change the position of a view in response to a dependent view changing, it
* should also implement <code>onLayoutChild</code> in such a way that respects those
* dependent views. <code>onLayoutChild</code> will always be called for a dependent view
* <em>after</em> its dependency has been laid out.</p>
*
* @param parent the parent CoordinatorLayout
* @param child child view to lay out
* @param layoutDirection the resolved layout direction for the CoordinatorLayout, such as
* {@link ViewCompat#LAYOUT_DIRECTION_LTR} or
* {@link ViewCompat#LAYOUT_DIRECTION_RTL}.
* @return true if the Behavior performed layout of the child view, false to request
* default layout behavior
*/
public boolean onLayoutChild(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, int layoutDirection) {
return false;
}
* Called when a descendant of the CoordinatorLayout attempts to initiate a nested scroll.
*
* <p>Any Behavior associated with any direct child of the CoordinatorLayout may respond
* to this event and return true to indicate that the CoordinatorLayout should act as
* a nested scrolling parent for this scroll. Only Behaviors that return true from
* this method will receive subsequent nested scroll events.</p>
*
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param directTargetChild the child view of the CoordinatorLayout that either is or
* contains the target of the nested scroll operation
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout initiating the nested scroll
* @param nestedScrollAxes the axes that this nested scroll applies to. See
* {@link ViewCompat#SCROLL_AXIS_HORIZONTAL},
* {@link ViewCompat#SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL}
* @return true if the Behavior wishes to accept this nested scroll
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onStartNestedScroll(View, View, int)
*联合滑动的方法监听
*/
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout,
V child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
return false;
}
* Called when a nested scroll has been accepted by the CoordinatorLayout.
*
* <p>Any Behavior associated with any direct child of the CoordinatorLayout may elect
* to accept the nested scroll as part of {@link #onStartNestedScroll}. Each Behavior
* that returned true will receive subsequent nested scroll events for that nested scroll.
* </p>
*
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param directTargetChild the child view of the CoordinatorLayout that either is or
* contains the target of the nested scroll operation
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout initiating the nested scroll
* @param nestedScrollAxes the axes that this nested scroll applies to. See
* {@link ViewCompat#SCROLL_AXIS_HORIZONTAL},
* {@link ViewCompat#SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL}
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedScrollAccepted(View, View, int)
*/
public void onNestedScrollAccepted(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child,
View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
}
* Called when a nested scroll has ended.
*
* <p>Any Behavior associated with any direct child of the CoordinatorLayout may elect
* to accept the nested scroll as part of {@link #onStartNestedScroll}. Each Behavior
* that returned true will receive subsequent nested scroll events for that nested scroll.
* </p>
*
* <p><code>onStopNestedScroll</code> marks the end of a single nested scroll event
* sequence. This is a good place to clean up any state related to the nested scroll.
* </p>
*
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout that initiated
* the nested scroll
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onStopNestedScroll(View)
*/
public void onStopNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target) {
}
* Called when a nested scroll in progress has updated and the target has scrolled or
* attempted to scroll.
*
* <p>Any Behavior associated with the direct child of the CoordinatorLayout may elect
* to accept the nested scroll as part of {@link #onStartNestedScroll}. Each Behavior
* that returned true will receive subsequent nested scroll events for that nested scroll.
* </p>
*
* <p><code>onNestedScroll</code> is called each time the nested scroll is updated by the
* nested scrolling child, with both consumed and unconsumed components of the scroll
* supplied in pixels. <em>Each Behavior responding to the nested scroll will receive the
* same values.</em>
* </p>
*
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout performing the nested scroll
* @param dxConsumed horizontal pixels consumed by the target's own scrolling operation
* @param dyConsumed vertical pixels consumed by the target's own scrolling operation
* @param dxUnconsumed horizontal pixels not consumed by the target's own scrolling
* operation, but requested by the user
* @param dyUnconsumed vertical pixels not consumed by the target's own scrolling operation,
* but requested by the user
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedScroll(View, int, int, int, int)
*/
public void onNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed) {
}
* Called when a nested scroll in progress is about to update, before the target has
* consumed any of the scrolled distance.
*
* <p>Any Behavior associated with the direct child of the CoordinatorLayout may elect
* to accept the nested scroll as part of {@link #onStartNestedScroll}. Each Behavior
* that returned true will receive subsequent nested scroll events for that nested scroll.
* </p>
*
* <p><code>onNestedPreScroll</code> is called each time the nested scroll is updated
* by the nested scrolling child, before the nested scrolling child has consumed the scroll
* distance itself. <em>Each Behavior responding to the nested scroll will receive the
* same values.</em> The CoordinatorLayout will report as consumed the maximum number
* of pixels in either direction that any Behavior responding to the nested scroll reported
* as consumed.</p>
*
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout performing the nested scroll
* @param dx the raw horizontal number of pixels that the user attempted to scroll
* @param dy the raw vertical number of pixels that the user attempted to scroll
* @param consumed out parameter. consumed[0] should be set to the distance of dx that
* was consumed, consumed[1] should be set to the distance of dy that
* was consumed
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedPreScroll(View, int, int, int[])
*/
public void onNestedPreScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
int dx, int dy, int[] consumed) {
}
* Called when a nested scrolling child is starting a fling or an action that would
* be a fling.
*
* <p>Any Behavior associated with the direct child of the CoordinatorLayout may elect
* to accept the nested scroll as part of {@link #onStartNestedScroll}. Each Behavior
* that returned true will receive subsequent nested scroll events for that nested scroll.
* </p>
*
* <p><code>onNestedFling</code> is called when the current nested scrolling child view
* detects the proper conditions for a fling. It reports if the child itself consumed
* the fling. If it did not, the child is expected to show some sort of overscroll
* indication. This method should return true if it consumes the fling, so that a child
* that did not itself take an action in response can choose not to show an overfling
* indication.</p>
*
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout performing the nested scroll
* @param velocityX horizontal velocity of the attempted fling
* @param velocityY vertical velocity of the attempted fling
* @param consumed true if the nested child view consumed the fling
* @return true if the Behavior consumed the fling
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedFling(View, float, float, boolean)
*/
public boolean onNestedFling(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean consumed) {
return false;
}
* Called when a nested scrolling child is about to start a fling.
*
* <p>Any Behavior associated with the direct child of the CoordinatorLayout may elect
* to accept the nested scroll as part of {@link #onStartNestedScroll}. Each Behavior
* that returned true will receive subsequent nested scroll events for that nested scroll.
* </p>
*
* <p><code>onNestedPreFling</code> is called when the current nested scrolling child view
* detects the proper conditions for a fling, but it has not acted on it yet. A
* Behavior can return true to indicate that it consumed the fling. If at least one
* Behavior returns true, the fling should not be acted upon by the child.</p>
*
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout performing the nested scroll
* @param velocityX horizontal velocity of the attempted fling
* @param velocityY vertical velocity of the attempted fling
* @return true if the Behavior consumed the fling
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedPreFling(View, float, float)
*/
public boolean onNestedPreFling(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
float velocityX, float velocityY) {
return false;
}
* Called when the window insets have changed.
*
* <p>Any Behavior associated with the direct child of the CoordinatorLayout may elect
* to handle the window inset change on behalf of it's associated view.
* </p>
*
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param insets the new window insets.
*
* @return The insets supplied, minus any insets that were consumed
*/
@NonNull
public WindowInsetsCompat onApplyWindowInsets(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout,
V child, WindowInsetsCompat insets) {
return insets;
}
}